Introduction:
Obesity has become a global health crisis, significantly impacting individuals, communities, and healthcare systems. Its prevalence continues to rise, leading to increased healthcare costs and the strain on medical resources. This blog will explore the multifaceted impact of obesity on healthcare costs, the resources required to manage it, and potential strategies for mitigation. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing effective interventions to address this complex issue.
The Economic Burden of Obesity:
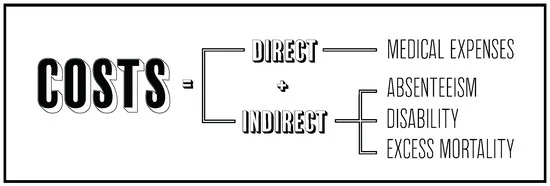
The financial implications of obesity are profound and multifaceted. The condition not only affects individuals’ health but also places a substantial economic burden on healthcare systems worldwide.
Direct Medical Costs: “Direct medical costs related to obesity include expenses for preventive, diagnostic, and treatment services. These costs cover a range of healthcare needs, from doctor visits and medication to surgical procedures like bariatric surgery. Obesity is a significant risk factor for numerous chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers, which require ongoing medical attention and contribute to high healthcare expenditures”. Says, Dr. Michael Broukhim, interventional cardiologist at Providence Saint John’s Health Center in Santa Monica, California.
Indirect Costs: Beyond direct medical expenses, obesity also incurs indirect costs. These include lost productivity due to illness, disability, and premature death. Employees suffering from obesity-related conditions are more likely to miss work and may experience reduced productivity when they are at work. Additionally, the economic impact extends to caregivers who may need to take time off work to support obese family members.
Healthcare Resource Allocation:
The rising prevalence of obesity demands increased healthcare resources, which can strain already burdened healthcare systems.
Increased Demand for Healthcare Services: “Obesity-related conditions require frequent medical consultations, diagnostic tests, and long-term management, leading to higher patient volumes in healthcare facilities. This increased demand can overwhelm healthcare providers and infrastructure, resulting in longer wait times and reduced quality of care”. Says, Dr. Beverly Tchang, assistant professor of medicine, endocrinologist, and advisor at Ro.
Specialized Care and Equipment: Managing obesity and its complications often requires specialized care and equipment. For instance, hospitals need to invest in larger medical equipment, bariatric surgical tools, and specialized beds to accommodate obese patients. Additionally, healthcare professionals require specialized training to effectively manage obesity-related conditions.
Chronic Disease Management:
Obesity significantly contributes to the prevalence of chronic diseases, which are major drivers of healthcare costs.
Diabetes: “Obesity is a leading risk factor for type 2 diabetes, a condition that requires lifelong management and incurs substantial healthcare costs. The treatment of diabetes involves medication, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, and management of complications such as neuropathy and cardiovascular disease”. Says, Says, Jamie Frew CEO, of Carepatron
Cardiovascular Diseases: “Obesity increases the risk of hypertension, coronary artery disease, and stroke. These conditions necessitate extensive medical care, including medications, surgeries, and rehabilitation. The cost of managing cardiovascular diseases is considerable, given the complexity and chronic nature of these conditions”. Says, Alex, CEO of Health Planner
Cancer: “Certain types of cancer, such as breast, colon, and endometrial cancer, have been linked to obesity. Cancer treatment is one of the most expensive areas of healthcare, involving surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and long-term follow-up care. The association between obesity and cancer further escalates healthcare costs”. Says, Rudy Bush, Founder at Wiringgerman
Psychological and Social Implications:
Obesity also has significant psychological and social implications, contributing to overall healthcare costs and resource utilization.
Mental Health: “Individuals with obesity are at higher risk of developing mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. These psychological issues often require therapeutic interventions, medications, and support services, adding to the overall healthcare burden”. Says, Makenna Francsis, PMHNP at American TMS
Social Stigma and Discrimination: “Obesity can lead to social stigma and discrimination, which can negatively impact mental health and access to healthcare. Stigmatized individuals may avoid seeking medical help due to fear of judgment, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment, and ultimately higher healthcare costs”. Says, Dr. Kim Langdon, an OB-GYN based in Ohio
Strategies for Mitigation:
Addressing the obesity crisis requires a multifaceted approach, involving individual, community, and policy-level interventions. Effective strategies can help mitigate the impact of obesity on healthcare costs and resources.
Preventive Measures: Prevention is key to reducing the prevalence of obesity. Public health campaigns promoting healthy eating, physical activity, and lifestyle changes can significantly impact obesity rates. Educational programs in schools, workplaces, and communities can raise awareness about the importance of maintaining a healthy weight.
Access to Healthy Foods: Ensuring access to affordable, nutritious foods is crucial in the fight against obesity. Policies that support the availability of fresh produce in low-income areas, subsidies for healthy foods, and restrictions on marketing unhealthy foods to children can promote healthier dietary choices.
Promoting Physical Activity: Encouraging regular physical activity through community programs, workplace wellness initiatives, and urban planning that supports active transportation (like biking and walking) can help reduce obesity rates. Access to safe parks and recreational facilities also plays a vital role in promoting an active lifestyle.
Policy and Public Health Initiatives:
Effective policy measures and public health initiatives are critical in addressing the obesity epidemic and its impact on healthcare costs and resources.
Healthcare System Reforms: Integrating obesity prevention and management into primary healthcare can enhance early detection and treatment. Training healthcare providers in obesity management and providing incentives for preventive care can improve patient outcomes and reduce long-term healthcare costs.
Legislation and Regulation: Implementing policies that regulate food marketing, labeling, and portion sizes can help control the consumption of unhealthy foods. Taxes on sugary drinks and junk food, combined with subsidies for healthier options, can shift consumer behavior towards better dietary choices.
Community-Based Programs: Community-based programs that focus on lifestyle changes, such as weight management classes, cooking workshops, and fitness groups, can provide support and resources for individuals trying to lose weight. Collaboration between public health agencies, local governments, and community organizations is essential for the success of these programs.
Technological Innovations:
Technology offers innovative solutions for obesity prevention and management, potentially reducing healthcare costs and improving resource utilization.
Digital Health Tools: Mobile apps and wearable devices that track physical activity, diet, and weight can help individuals monitor their progress and stay motivated. Telehealth services can provide remote counseling and support for weight management, making healthcare more accessible and reducing the need for in-person visits.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics: AI and data analytics can help identify trends and risk factors associated with obesity, enabling targeted interventions. Personalized treatment plans based on an individual’s health data can improve outcomes and reduce unnecessary healthcare costs.
Behavioral Interventions: Technology can support behavioral interventions through gamification, social networks, and virtual support groups. These tools can enhance engagement and adherence to weight management programs, leading to more sustainable results.
Conclusion:
Obesity’s impact on healthcare costs and resources is profound and multifaceted, affecting not only individuals but also the broader healthcare system and economy. Addressing this complex issue requires a comprehensive approach that includes prevention, early intervention, and ongoing management. Public health initiatives, policy reforms, and technological innovations all play crucial roles in mitigating the impact of obesity.
By promoting healthy lifestyles, ensuring access to nutritious foods, encouraging physical activity, and leveraging technology, we can make significant strides in reducing obesity rates and alleviating its burden on healthcare systems. Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, policymakers, communities, and individuals are essential for creating a healthier future and managing the economic and resource challenges posed by obesity.